Cotton fabric occupies a leading position in the world due to its versatility, practicality and hypoallergenicity; it is used in almost all areas of life. Dense fibers look attractive and allow you to create colorful elegant and everyday items for any season. Everything that is useful to know about cotton is described below.
- History of Cotton
- The birthplace of cotton fabric
- Composition and structure
- Production technology: stages
- The difference between cotton and other natural fabrics
- How to distinguish linen fabric from cotton
- Types of fabrics and their characteristics
- Types of weaves of cotton fabric
- Twill weave
- Types of cotton fabrics by finishing method
- What can be sewn from cotton fabric
- Care of cotton products
- Advantages and disadvantages of cotton
- Price overview
History of Cotton
Cotton fabric is one of the first linen products on Earth. Man began cultivating cotton about 15,000 years ago. The first descriptions of the plant are found in Indian writings, where the material was highly valued along with decorations. Today, products from Egypt more than 5,000 years old have survived, confirming the strength of natural fibers.

Cotton fabric came to Europe as early as the 1st century AD, the material was highly valued, and cotton began to be grown in many regions. The fabric appeared on Slavic lands in the 15th century, but since then it has occupied one of the main positions, and in the 20th century it already accounted for ¾ of all textile production. Today, a third of cotton consumption in the world is in China, and the main suppliers have become the United States and African countries.
The birthplace of cotton fabric
The natural habitat of cotton and its birthplace is considered to be Asia Minor, where the processing of the plant began, creating a soft white fabric. With merchants, cotton came to North African countries, Greece and the Mediterranean. There, the properties of the durable, lightweight material were highly appreciated and the cultivation and processing of plant materials began to be mastered.

Initially, cotton was not dyed or bleached. Only high-ranking persons could afford bright clothes dyed with expensive dyes. Indigo was considered the most valuable - a deep purple extract, also coming from the Arabian Peninsula. Much later, textile production began to gain momentum and spread throughout the world, offering more and more new solutions.
Composition and structure
Classic cotton fabric consists of 100% natural cotton, but modern production allows mixing different types of raw materials in their composition, insulating, adding elasticity to the material and reducing the cost of the finished product. Cotton is usually combined with other organic fibers - flax, wool, or with synthetics - acrylic, viscose, polyester and other fibers.
This is interesting! At first glance, the strange name of the fabric is associated with the smell of its fibers. When burning, cotton emits a papery aroma, similar to dry wood, which is what gave rise to the generally accepted name of the material.
Cotton is highly durable, hygroscopic and hypoallergenic, easy to dye and very convenient to sew - does not slip, washes and irons well. Thanks to these characteristics, the material remains popular and in demand to this day, and the variety of its varieties continues to grow.

Production technology: stages
Fine cotton fibers are obtained from the seed pods of the plant. They are first collected by hand or machine, formed into large fluffy bundles and sent to production. These lumps are called raw cotton. It can be white, milky or pinkish.
Next, the cotton is cleaned of husks, seeds, and husks, sorted by fiber length, and twisted into solid continuous threads, producing yarn. All types of fabrics are woven from it.

In some cases, the threads are bleached and dyed beforehand, but more often, the finished fabric is subjected to such treatment. It is bleached and then dyed in different ways. For example, a printed print can be colorful and motley, and monochrome dyeing can be smooth and "boiled".
The difference between cotton and other natural fabrics
It is quite difficult to single out cotton among other natural fabrics using a single criterion, but a pairwise comparison helps to form an idea of the material:
- Cotton fabric absorbs light, while silk, linen and even wool have a slight natural sheen.
- Cotton is soft but warm, while silk creates a cooling effect and wool provides intense warmth.
- Cotton is the most breathable of all fabrics; it easily lets air through, absorbs body moisture, and dries fairly quickly in the sun.
- Smooth, thin cotton fibers are evenly dyed, which is why so many different types of fabric can be easily created from them.

How to distinguish linen fabric from cotton
There are several visual signs to distinguish dense cotton fabric from linen:
- Cotton is obtained from the soft fibers of the plant capsule, it is similar to cotton wool, so the material is soft and gentle to the touch. Flax is made from the stems of the plant, so the fabric is rough, uneven and slightly embossed.
- The color of natural cotton is pure white with possible shades, and undyed linen fabric is similar to straw - it has a grayish color with a golden or brown shade. At the same time, pure cotton has a matte shade, and linen has a characteristic shimmer.
- Despite the strength of cotton, it is still delicate and over time the threads can burst and break. Linen products serve for decades without wearing out, they hold their shape perfectly. At the same time, sewing from such fabric is quite difficult.

Please note! The most reliable way to check is by touch: flax will be harder. Visually, its fibers are thicker, flatter, creating a feeling of pressing.
Types of fabrics and their characteristics
Cotton fabric is made from cotton fibres - hollow, elongated structures that are twisted into thread. Three types are used in production:
- Short - from 20 mm, they produce "loose" types of fabric with a non-uniform structure, like flannel. They stretch, create an air cushion and warm in cold weather. Over time, their surface rolls up.
- Medium - about 30 mm. Such threads produce light summer fabrics that are distinguished by good "breathing" and hygroscopicity.
- Long - up to 50 mm in length, due to which the fabric is smooth and very durable. Such products do not lose their shape for a long time, maintaining neatness and an impressive appearance.

It is also necessary to note that among the types of cotton fabrics there are natural and mixed. Acrylic, polyester and other fibers are added to natural fiber to increase the elasticity of the material, and cotton is mixed with wool to insulate the fabric.

Types of weaves of cotton fabric
Cotton material is woven with different types of fiber weave. There are three main options:
- Linen - a classic type, where the threads are intertwined sequentially and form a smooth, even surface. Such fabric is durable and effective. Examples of linen cotton are calico, poplin, chintz, cambric.
- Satin - shiny fabrics with weft threads on the surface. Such materials look festive and sophisticated. In addition to satin itself, this includes, for example, eraser.
- Twill - coarse, strong and slightly loose fabrics with a shift in threads. Among them are flannel, denim, tartan.
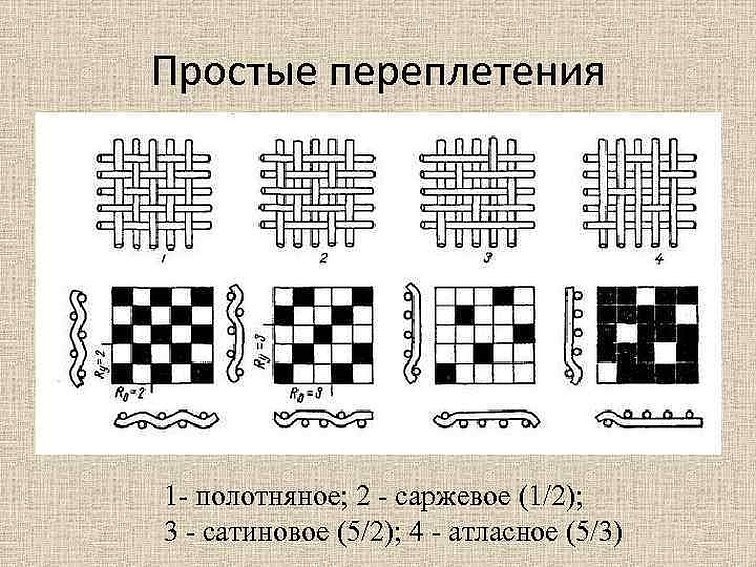
All these types of weave of weft and warp give very different types of cotton natural fabric, and even within one of them there are very different varieties. Each fabric finds its specific application in the sewing and textile industry.
Twill weave
Twill weave materials are characterized by increased strength, durability and pleasant softness. They are usually used to make not only clothes - jeans, jackets, blazers - but also furniture upholstery, drapery, linings.
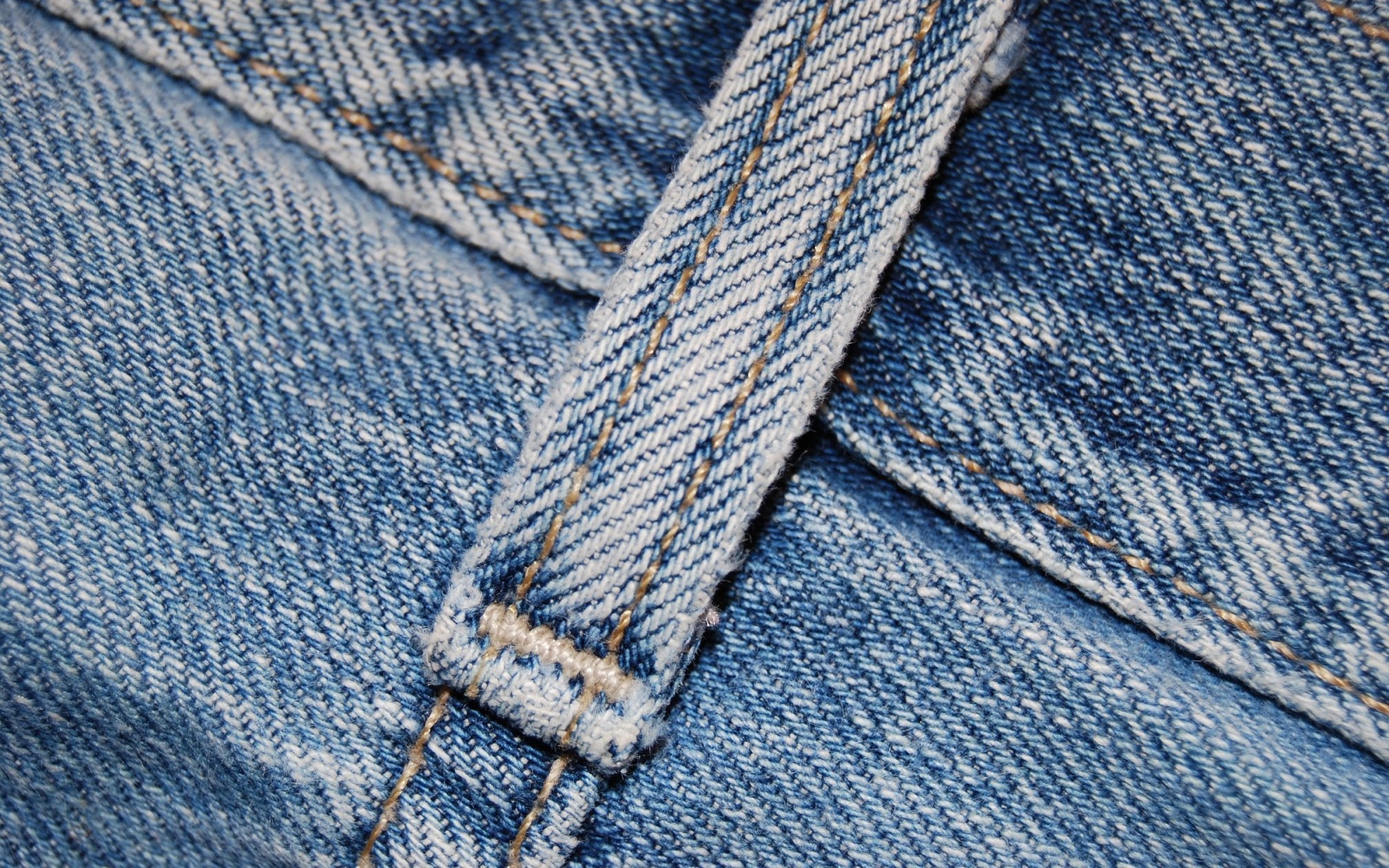

One of the most popular varieties was denim, which eventually gave birth to everyone's favorite jeans. In the first case, the fabric with a characteristic "rib" is dyed in any shade, but jeans are a specific type. This option is not dyed a second time, but the material is woven from pre-dyed threads. In the classic view, jeans capture all shades of indigo, but gray, green and other shades have long been produced.
The second type is flannel, a soft fabric with a light brushed finish on one or both sides. It is usually used to make home and comfortable everyday clothes, and sometimes thin blankets.
Bumazeya is a smooth, warm material with a one-sided nap. It is also used to decorate home textiles, because such cotton (napped) gives warmth, softens surfaces and looks impressive.
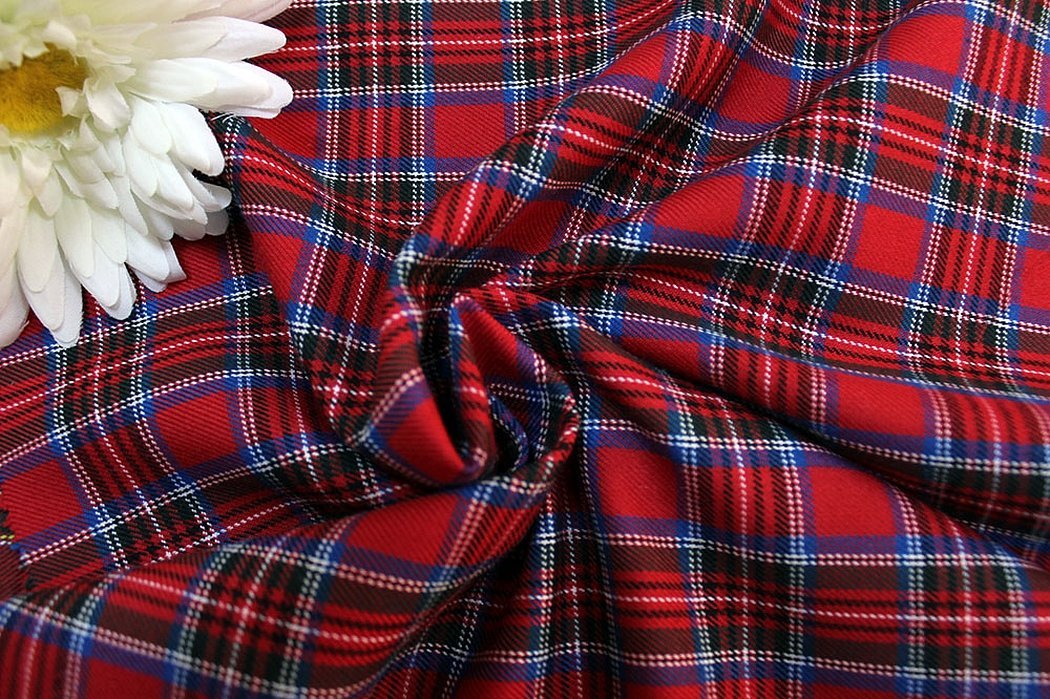

Tartan is "that" well-known dense and representative cotton fabric in a check. From which traditional kilts, suits, skirts and other items are sewn.
Types of cotton fabrics by finishing method
To improve the useful and aesthetic qualities of the material, it is processed in several ways depending on what kind of cotton fabric it is. The preparatory stage means a lot: a special impregnation makes the fibers more durable, wearable and impressive in appearance.
- Raw fabrics are those that cannot be processed in any way.
- Bleached cotton is used in the production of linen, when dyeing fabrics in light and bright shades.
- Mercerized fabric is used for blouses, shirts and dresses, since the process allows the products not to shrink after washing and to better absorb moisture.
- Insulated fabrics are decorated with pile - flannel, fustian, baize, terry.
- According to the dyeing method, cotton can be plain-dyed - by soaking, printed - that is, with a pattern stamp, or multi-colored - including multi-colored threads.

What can be sewn from cotton fabric
Cotton is versatile, so you can sew any item from it - from simple pillowcases to a three-piece suit. Most often, summer dresses and trouser suits, medical or other special uniforms, and shirts are sewn from cotton.
Making a set of bed linen or beautiful curtains is also not a problem. There is no need to compromise and overpay for branded products - you can buy material with a print you like from a premium or economy class and implement your unique ideas.
Care of cotton products
Cotton is not too demanding in care, but in order for things to last longer, you should follow the basic recommendations:
- To prevent items from shrinking, wash them at temperatures up to 60°C, and do not treat colored items with bleach.
- Dry cotton, carefully spread out, on hangers or a net to avoid the formation of creases that are difficult to smooth out.
- The iron temperature should not exceed 200°C, and cotton is ironed with steam so that the fabric does not burn, does not become sealed and looks soft.
- It is better to wash cotton items separately from synthetics and other fibers, then the surfaces will not wear out and become worn.

Important! If stains appear, they should be washed immediately in cool water, and then with soap in warm water, until the coloring pigments (wine, coffee, ink) are absorbed deep into the fibers.

Advantages and disadvantages of cotton
Despite the huge variety of cotton fabrics, they all have positive properties of fibers and some disadvantages. Among the obvious advantages are the following:
- High hygroscopicity and breathability. Thanks to these qualities, cotton can be worn in hot weather.
- Durability and abrasion resistance. Most cotton materials do not shrink, do not fade for a long time, and are resistant to tension. Therefore, they serve for a long time, remaining neat.
- Ease of processing. Cotton responds well to dyeing, is easy to cut and machine sew, and is easy to wash and iron.
- Hypoallergenic and pleasant texture. The fabric does not cause irritation, does not rub the skin and is suitable even for children.

Some notable shortcomings:
- Cotton tends to wrinkle and crease, making it difficult to fit clothes exactly to your figure. When washing in hot water, the material may shrink.
- The fabric is not elastic.
- Natural and eco-friendly types are expensive.
Important! To solve the above-mentioned problems, extend the life of cotton items and create beautiful models, synthetic fibers are added to the material in an optimal ratio, which is why the products do not lose their positive properties and only benefit.
Price overview
Cotton prices generally remain stable - it is relatively inexpensive and comfortable to work with in every sense.
In the first half of 2019, prices are as follows:
- cambric can be purchased for 500-800 rubles/running meter;
- fabric for shirts, suits and dresses within 800-1600 rubles/running meter;
- first-class European fabrics from France and Italy - from 400 to 2500 rubles/running meter;
- rags and fabrics for lining and bed linen from 20 rubles/running meter.

Since cotton fabric remains one of the most durable and pleasant to the body, there is always a demand for all its types. Today, you can easily collect beautiful material and sew something special and unusual with savings.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o8s7Fh6tfmk




