Genuine leather is a material that has served humanity since the beginning of time. It was used to make clothes, armor, bags, waterskins, and parchment for books. But at all times, this material was not cheap. In addition, modern trends in humanism and concern for the environment lead to a decrease in demand for genuine leather. Eco-leather is the best solution to this problem.
- What is eco-leather and what is it made of?
- Eco-leather: history of origin
- Properties, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of the material
- The difference between leather and eco-leather
- Comparison of vinyl leather and eco-leather
- How to distinguish eco-leather from other analogues
- Using ECO leather
- Eco-leather car seat covers
- Eco-leather shoes
- Eco-leather bags
- Furniture production
- Eco-leather: tips and recommendations for care
What is eco-leather and what is it made of?
A person unfamiliar with this material will ask, upon hearing the word eco-leather, what is it? A new name for leatherette? And most will quickly be convinced that this is exactly so. Because of this, eco-leather items are not in demand. And frankly in vain.
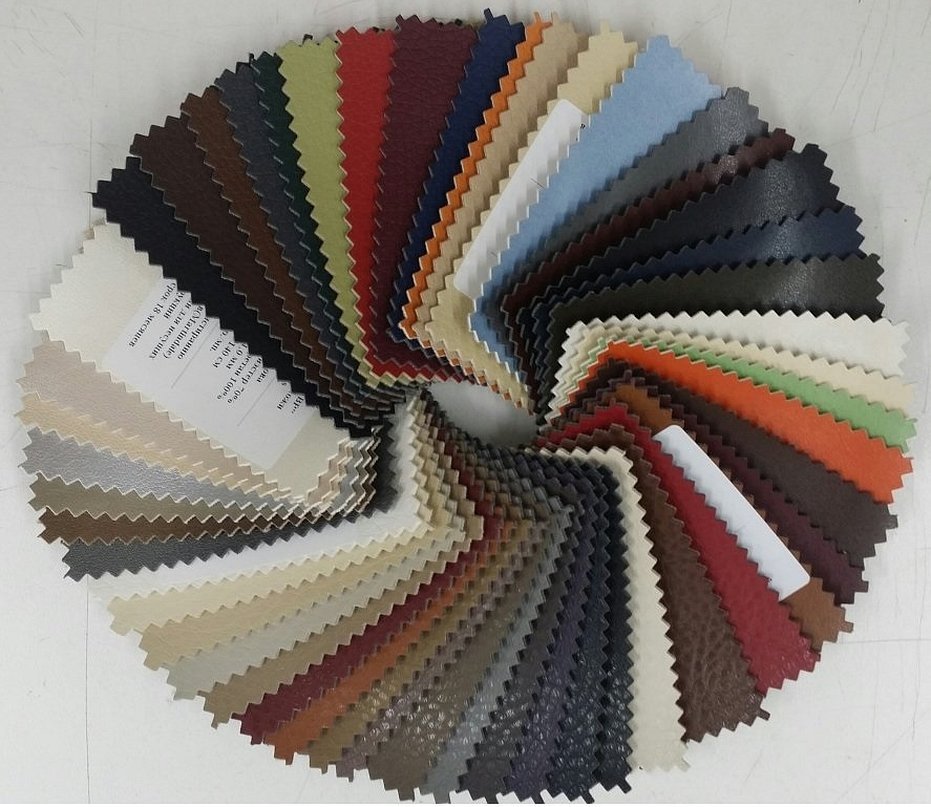

Eco leather is a fabric. It consists mainly of cotton, for higher quality products, or polyester, for greater cheapness, or when the base material does not matter. Much less often, other natural materials are used for this, such as linen, etc. A very thin layer of polyurethane is applied to the fabric base.
This is what gives the material the prefix "eco". Its safety for humans and the environment is shown at least by the fact that implants are made from it. After application, the layers are connected and textured for the required tasks through special shafts.

Occasionally, you come across "eco-leather" with a pressed leather base. In fact, if you figure out how pressed leather is made, the prefix "eco" should be, at the very least, crossed out. What eco-leather means, as a name, is justified only by a layer of polyurethane. But in this case, the material turns out to be worse in some ways than with a cotton base.
The advantage is greater wear resistance and significantly less visible damage. But only if the colors of the outer and inner layers match. Also, leather particles are often sprayed onto the inner side. This fabric is not distinguished by anything special except its appearance.
Eco-leather: history of origin
First, we need to understand the difference between eco-leather and leatherette. Attempts to create a cheaper analogue of natural leather have been going on for a long time. The very first versions were incredibly far from the natural analogue and were made of rubber. The first patents for the production of artificial leather date back to the end of the 19th century, and large-scale production was launched around the 1930s.
This artificial leather was made from nitrocellulose fiber applied to fabric. The material was used both as a leather substitute and as an inexpensive finishing material, covering doors or tabletops with it. But leatherette did not live up to expectations. The speed of its wear, peeling and low quality in principle played their role. A rather unflattering distortion of the name (with the addition of a soft sign at the end of the first syllable) has become established among the people as a reflection of its quality.

Around the 1950s and 1960s, leatherette was pushed out of the market by its higher-quality analogues — amido leather and vinyl leather, based on polyamide and PVC, respectively. However, by that time the word "leatherette" had become a household word, and now it is used to refer to almost all types of leatherette.
Eco-leather, which has a composition of fabric and a layer of polyurethane, was first produced in 1963 in the USA, and then, independently of them, in 1964, similar results were achieved in Japan.
Properties, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of the material
First of all, the characteristics, and therefore what eco-leather is, are determined by the materials used and their ratio. The wear resistance, tactile component and density of the fabric depend on the thickness of the polyurethane. And from this - the scope of application.
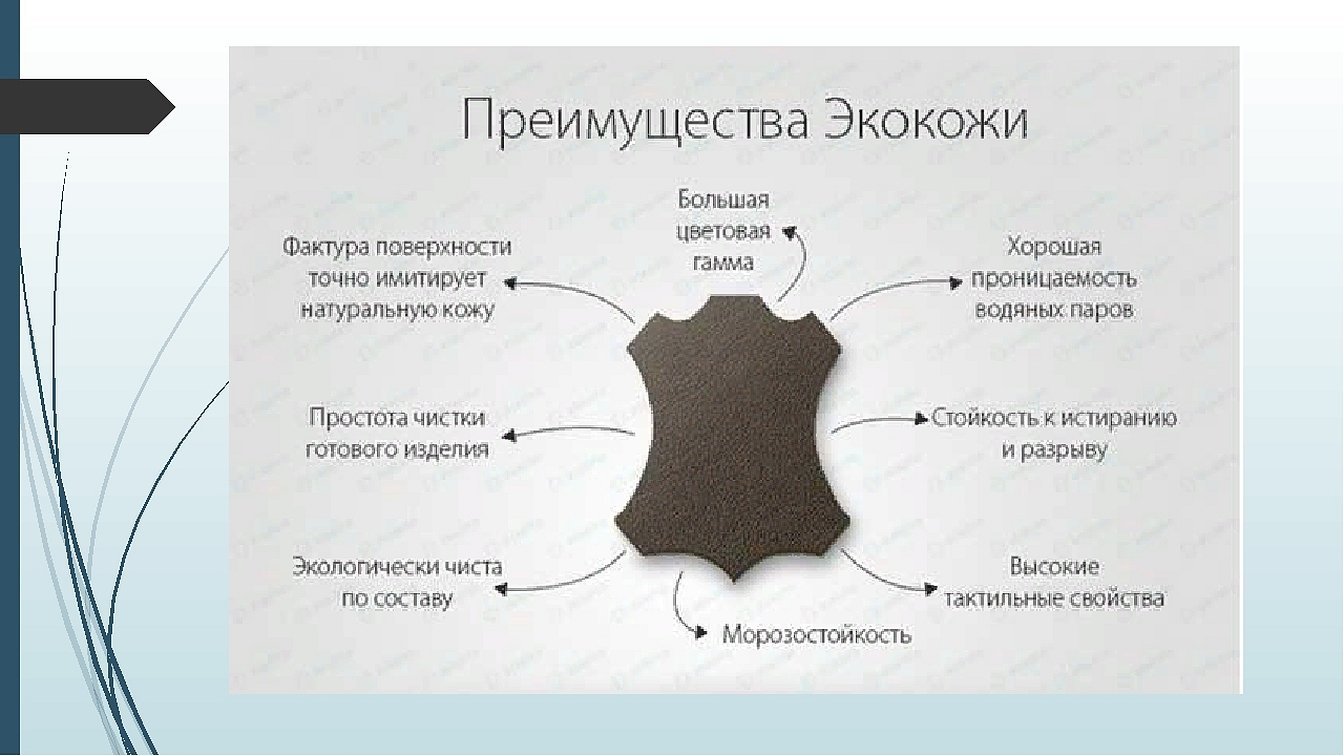
Without going into specific cases of different types and brands, the following features can be highlighted:
- Temperature conditions. The temperature limit declared by many manufacturers is from -35 to +50 degrees. But in fact, eco-leather can withstand even more significant readings from -50 to +80.
- Wear resistance. Polyurethane is used to make everything from shoe soles to sports car tires, which speaks for itself.
- Aesthetic diversity. Eco-leather can have absolutely any color and texture.

- Hypoallergenic. Can be worn by people with allergies to skin and fur.
- Dimensions. It is not a problem to buy a roll 25 meters long and 1.5 meters wide, which is impossible to do with genuine leather.
- Air permeability. The fabric breathes freely due to the microporous structure of the polyurethane layer.
- Hygroscopicity. The same microporosity allows steam to escape, and moisture does not linger on the inner layer.
- Eco-friendliness. The production of eco-leather requires fewer chemicals and is less harmful to the environment even compared to regular leather.
- Cheapness. Everything is relative, of course, but if you compare it with genuine leather, the leader will be immediately visible.
- The material does not stretch.
- Does not fade in the sun.
- Durability. If compared to leather of the same thickness, it will be easier to tear genuine leather.

There are also disadvantages and some of them make you think separately about the advisability of using eco-leather in various conditions. Of the obvious disadvantages, it is worth noting:
- If not properly cared for or the top layer is accidentally damaged, the fabric quickly loses its performance properties.
- Any mechanical damage exposes the fabric base of the material.
- Eco-leather is considered non-repairable. Most often, it is easier to replace the entire canvas, especially in case of large-scale damage.
- Some stains, such as felt-tip pen marks, are difficult to remove.
The difference between leather and eco-leather
There may be many reasons to choose one material or another, but due to the difference in price, unscrupulous sellers will always take advantage of the inability to distinguish them. Unlike older analogues, eco-leather is very difficult to distinguish from leather tactilely.
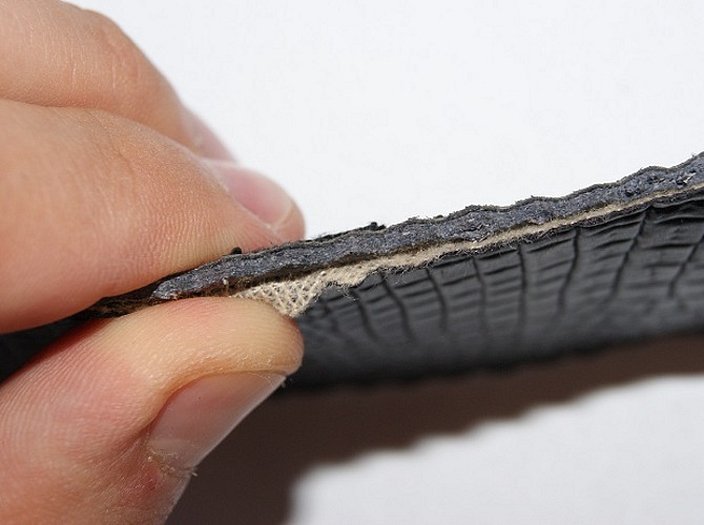

Moreover, eco-leather is more likely to be pleasant for hands than natural leather. Except perhaps for aniline leather, which is much more difficult to find, as it is more expensive. The reason is the substances that are used to treat natural leather during production. In any case, there is always a way to get to the truth:
- There must be a tag made of a piece of leather, in the shape of a skin. For leather goods this is a mandatory attribute.
- Pay attention to the back of the material. If there are many threads, then it is definitely not genuine leather. But given the technology of spraying leather microparticles, the method does not always work.
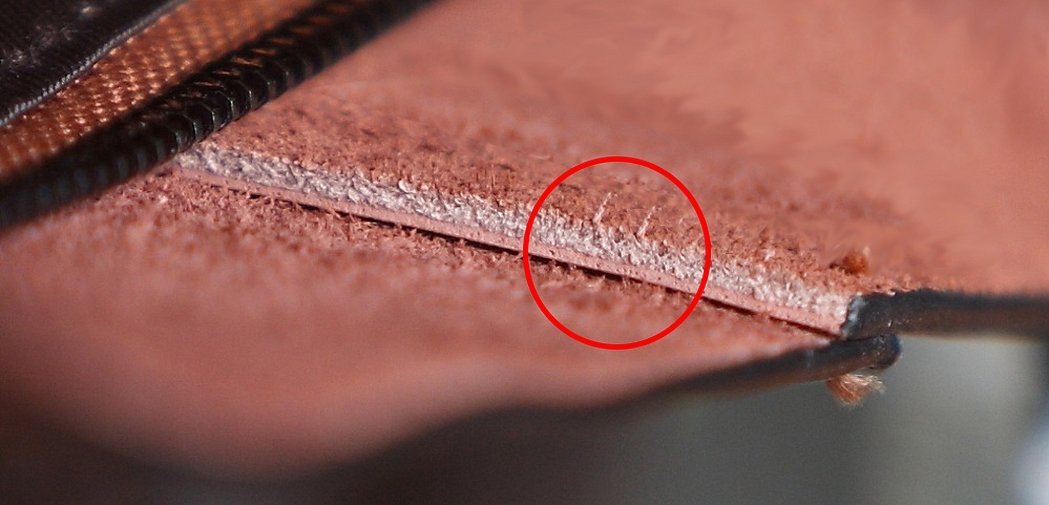
- Find the edge of the material. This can be problematic, as the edge of artificial leather is most often folded and hidden in the seam. Check all the joints and along the zippers. If threads stick out or are simply visible from the edge of the material, and the upper face layer has a porous structure, then the material cannot be called natural.

- When in contact with the body, genuine leather will warm up faster and cause more active sweating than eco-leather.
- Bend the product. The leather gathers in folds and may change its shade.
There are also methods that are somewhat more controversial and extreme. Checking in this way can only be done with the full consent of the persons.
- Fire. Faux leather will not pass the fire test. The smell of burnt synthetics and rubber is very different from the smell of burning leather. In addition, it is much more difficult to set fire to natural leather. But dyes and other leather treatments can help with this, so it is better to heat from the inside. However, the seller must agree to this, and the method is not suitable for every type of eco-leather.
- Water. Faux leather will not absorb water. But it is also easy to treat genuine leather with a water-repellent compound.
- Allergy sufferers. As strange and inhumane as it may be, you can find a person with an allergy as a kind of detector.
Please note! It is useless to trust the smell. Methods for aromatizing artificial leather have long been developed and their use is not new.
Comparison of vinyl leather and eco-leather
The active introduction of eco-leather reduces the importance of vinyl leather, but it has not been possible to completely displace it from the market. If we consider the difference between eco-leather and artificial leather, the disadvantages of leatherette are the first to catch the eye.
- Vinyl leather does not breathe. The PVC layer that imitates leather does not have a porous structure and does not allow air or water to pass through.
- When heated, it releases harmful and toxic substances
- The material is "colder" than eco-leather. And the colder it is around, the more noticeable the difference.
- Afraid of solvents.
- PVC itself is afraid of long-term exposure to UV rays, and adding various additives does not completely protect against this.
In principle, the properties of vinyl leather depend on the manufacturing technology and materials used, due to which it is possible to achieve a wide range of results. From resistance to alkalis and acids to resistance to temperatures from -40 to +200. But such material is not made for sewing jackets and sneakers.
How to distinguish eco-leather from other analogues
Since there are quite a few different materials that replace leather, it is easy to get confused, which is demonstrated by the fear of buyers using different types of artificial leather. Let's try to figure out how eco-leather differs from other leatherette.

- Subjective sensations. The tactile sensations of eco-leather are no worse, and sometimes even superior to leather. Leatherette feels like plastic in the hand.
- Vegetable oil. This method will work if you have a day to spare. Apply vegetable oil to the material and leave it for a day. Eco-leather will absorb the oil without any problems, but the plasticizers of the leatherette will be in trouble, the material will become rough and hard in the place of application. This process is not reversible, so you need to act with caution.
- Freezing. Leatherette will not withstand low temperatures and will crack. Eco-leather will not change its qualities even at -30.
- The presence of a sharp, chemical smell immediately indicates that this is not eco-leather. But the method does not always work.
Using ECO leather
Eco-leather has found its place in the same areas where its natural analogue is used. These are clothes, haberdashery, furniture upholstery, car covers and interior upholstery, footwear and even wall decoration. Sometimes, for some needs, eco-leather becomes preferable to its natural analogue.

For example, to understand what eco-leather for clothing is, imagine what it is like to be in a leather jacket on a warm day in the sun. The leather heats up and sticks to the sweaty body. Eco-leather has a higher vapor permeability, which allows you to avoid such inconveniences.
Eco-leather car seat covers
A separate advantage of such covers is the absence of "sweating". In hot weather, the seat does not stick to exposed parts of the body, and the body itself sweats noticeably less. In addition, it is noticeably lighter than natural leather, which, albeit slightly, will make the car lighter.
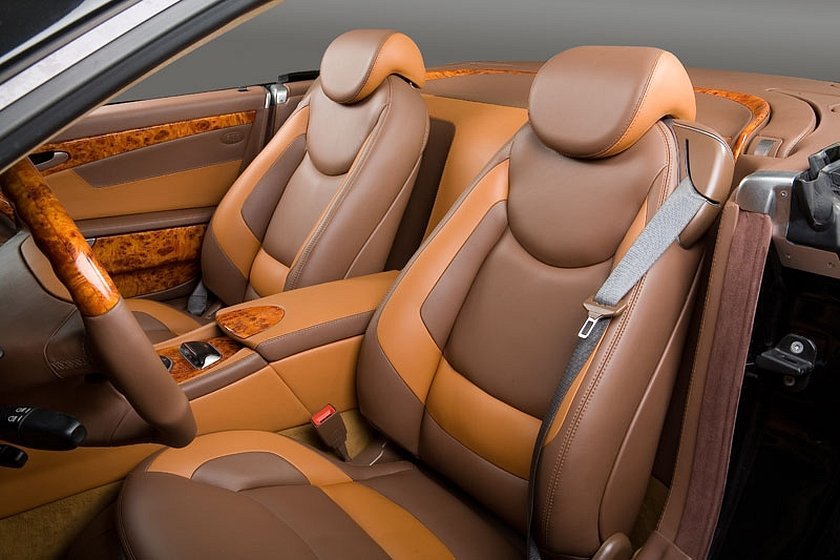

Various texture and color options are also possible, which will allow you to design the interior according to your personal preferences. And this at a significantly lower price. And unlike leatherette and vinyl leather, it does not emit foreign and toxic compounds when heated. However, the following disadvantages spoil the picture:
- Heating car covers in summer and cooling in winter. Climate control can handle this, but it will take time.
- Does not like the use of chlorine, responding to it by losing color.
Eco-leather shoes
This woven material is colder than real leather and survives frosts more difficult. But this does not matter when making summer and demi-season shoes. But a higher breathability is a plus. In the heat, the foot feels more comfortable in them. Any designer will answer the question: "Eco-leather, what kind of material is this for shoes?" This is freedom and the opportunity to experiment with color and texture, which gives a huge selection of shoes of all types and colors. You can take care of it in the same way as shoes made of ordinary leather.

Eco-leather bags
Much cheaper, noticeably lighter and at the same time absolutely any type, style and color. You can choose eco-leather for a snake, ostrich, calf and anyone. Frost resistance is suitable for residents of middle latitudes. And not a single animal suffers.

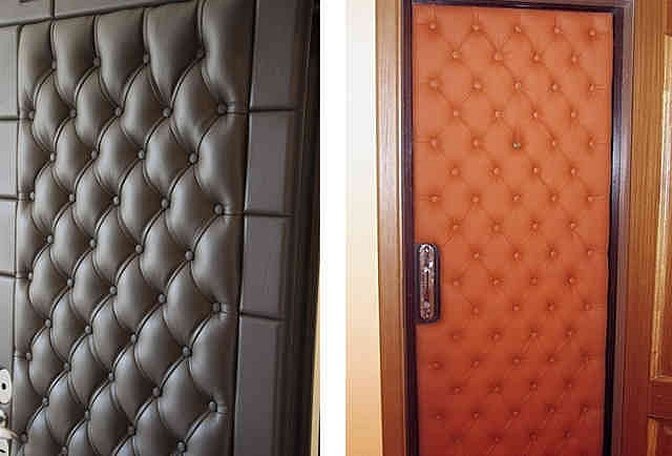
Furniture production
Furniture with eco-leather elements is not new. It is used as upholstery for soft furniture, and as a cover for hard parts. Unlike a sofa made of genuine leather, the body sweats much less on an eco-leather sofa, and the furniture will look exactly the same. But it must be protected from pets, since traces of claws or teeth will be fatal for the material. The polyurethane layer will begin to quickly come off the fabric base.

Only reupholstery can save the situation. For designers, it is clear what eco-leather is for shoes, furniture, decoration and clothing - these are new opportunities to realize themselves and their ideas.
Eco-leather: tips and recommendations for care
First of all, it is worth noting that a line of care and cleaning products has already been created and is being sold for eco-leather. For household conditions, it is better to remember the following:
- Use a water-repellent impregnation. It can be easily and inexpensively purchased as a spray in shoe stores.
- Eco-leather should be kept dry. Therefore, if the fabric gets wet, it is worth wiping it with a soft cloth. It is better not to use waffle towels and hard fabrics, so as not to accidentally damage the polyurethane layer.
- Heavy dirt can be removed with a 40-50% alcohol solution. Or just vodka.
- You can take it to the dry cleaner.

In conclusion, we can once again answer the question: eco-leather, what kind of material is it? First of all, it is a modern replacement for natural leather. Its properties are not inferior to natural leather, and in some ways they are superior. Especially in the matter of preserving the environment. But, as they say, if something works well, it will not mean that improvements cannot be made.
Science is rapidly developing, gaining momentum and accelerating day by day. What the coming day will bring us is unclear. And the question: "What is better, eco-leather or leather?" remains open, but at the moment eco-leather is the best of all options to replace natural leather.




